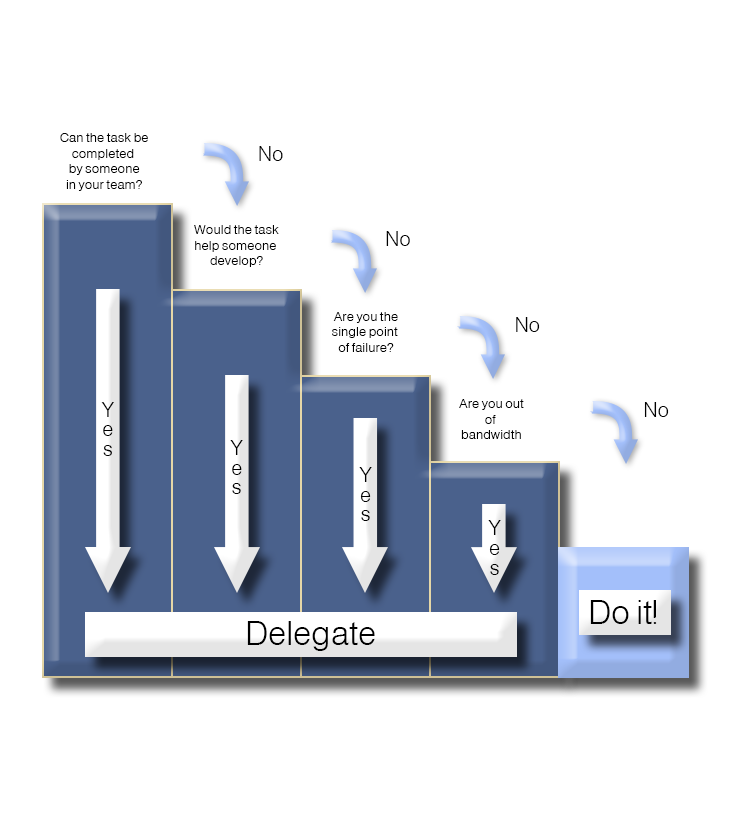
The Delegation ‘Stepping’ Model
The Delegation ‘Stepping’ Model builds on traditional delegation frameworks by encouraging leaders to delegate as much as possible, maximizing efficiency, scale, and impact. Illustrated as a staircase with descending steps, it integrates key considerations: Assess Capability, Match Task, Set Expectations, Provide Support, Monitor Progress, and Review Growth. This model shifts the focus from urgency and importance to building team resilience, reducing single points of failure, and ensuring leaders focus on their core leadership role.
Understanding the Model:
Core Philosophy: Unlike conventional models that prioritize tasks by urgency or importance, this model advocates delegating to capable team members, freeing leaders to tackle strategic priorities. It’s not about avoiding work but achieving maximum impact through team empowerment.
Structure: The staircase guides the delegation process:
Assess Capability: Evaluate team members’ skills and potential to handle tasks.
Match Task: Assign work to those best suited, delegating nearly everything feasible.
Set Expectations: Clearly define goals, deadlines, and standards.
Provide Support: Offer resources, guidance, or training as needed.
Monitor Progress: Check in periodically to ensure alignment and address issues.
Review Growth: Assess outcomes and team development, reinforcing capabilities.
Purpose: This model aims to build a resilient team, reduce dependency on individual leaders, and develop skills across the board. It challenges the mindset of leaders doing tasks themselves—often because they believe they can do it better—reminding them they’re paid to lead, not to execute.
Impact Focus: By delegating broadly, leaders avoid becoming bottlenecks, fostering a culture of trust and growth while focusing on high-level responsibilities.
This approach redefines delegation as a strategic tool for leadership success and team empowerment. The Delegation ‘Stepping’ Model offers actionable steps to enhance leadership and team development:
Capability Review: Start with Assess Capability—list team members’ strengths and identify tasks they can handle.
Task Assignment: Use Match Task to delegate widely—e.g., assign routine reports to a capable junior, reserving strategic planning for yourself.
Clarify Goals: Set Expectations by outlining deliverables (e.g., “Complete by September 10, 2025, at 02:03 PM IST”).
Offer Support: Provide Support with resources or check-ins, ensuring success without micromanaging.
Track Progress: Monitor Progress with brief updates (e.g., weekly stand-ups) to stay informed.
Evaluate Growth: Review Growth post-task—discuss what was learned and how skills improved.
Team Engagement: Involve the team by discussing delegation plans, encouraging ownership of assigned tasks.
Leadership Focus: Regularly audit your workload—delegate more to focus on leadership priorities like vision-setting.
By applying the Delegation Stepping Model, leaders can build a robust, capable team, reduce single points of failure, and ensure they fulfill their strategic role, driving maximum impact for their organization.